[This post is an excerpt from a recent TSI commentary]
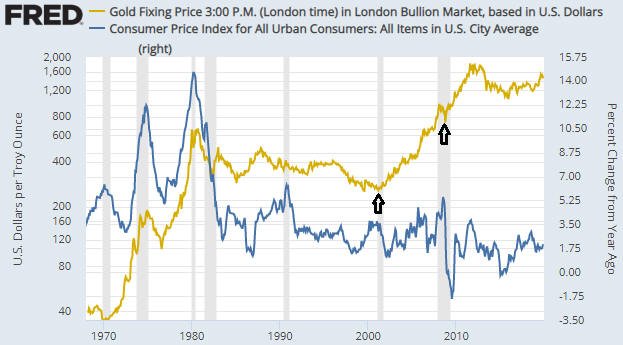
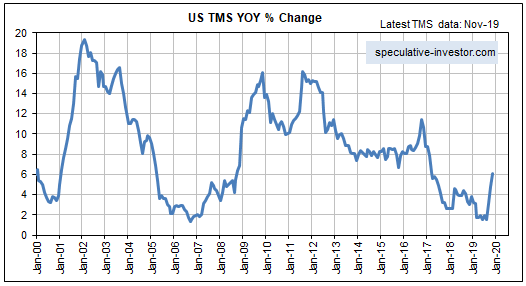
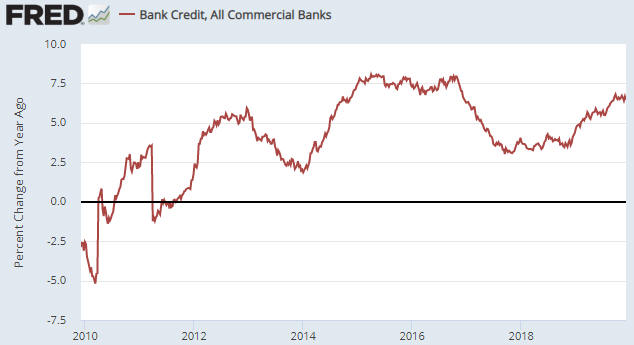
Over the past three months the year-over-year rate of growth in US True Money Supply (TMS), a.k.a. the US monetary inflation rate, has jumped from a 12-year low of 1.5% to a 2.5-year high of 6.1%. Refer to the first of the following charts for the details. This is due to the combination of the Fed’s new money-pumping scheme, which we are told is not QE even though it is identical to QE in terms of its effect on bank reserves, the money supply and the financial markets, and the expansion of commercial bank credit at close to its fastest pace in 10 years. The second of the following charts shows the year-over-year rate of change in commercial bank credit. If the commercial banking system continues to expand credit at the current pace and the Fed runs its new asset monetisation program until at least the end of March, then by the third quarter of next year the US monetary inflation rate will be above 10%. What does this mean for the financial markets and the economy?
Once a boom turns to bust there is nothing the Fed can do to stop or even delay the hardship that most people experience during periods of economic recession or depression. There also is very little the Fed can do after the boom-bust transition has occurred to prevent asset prices from tumbling. However, before the boom collapses, as eventually it must, it can be given a second (or a third or a fourth or a fifth) wind by a substantial new injection of money. Therefore, IF the boom is still mostly intact then the strong rebound in monetary inflation could prolong the cycle.
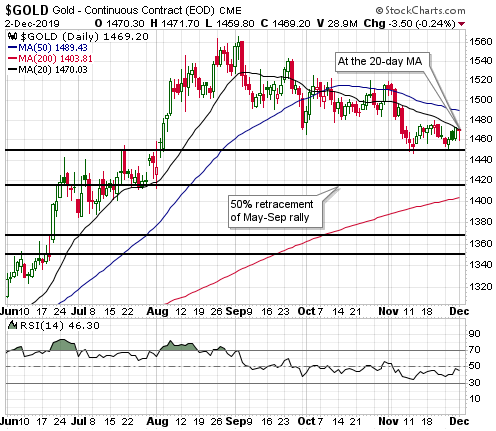
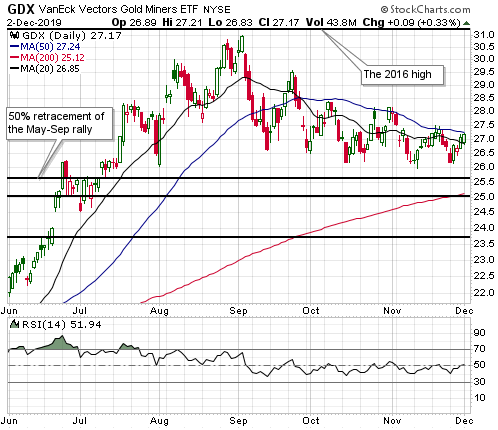
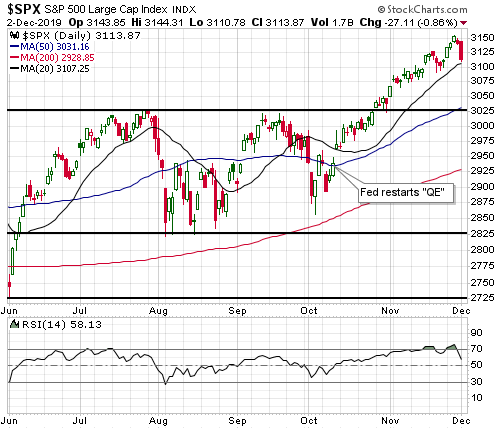
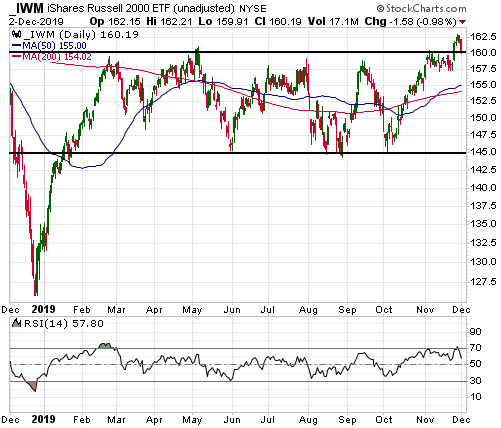
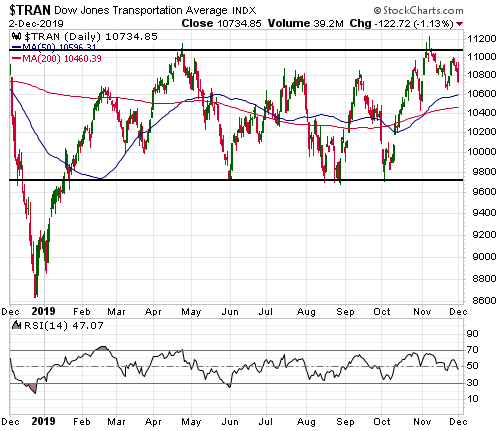
Given that the senior US stock indices are at all-time highs in dollar terms and are yet to signal long-term downward reversals in gold terms, it’s possible that the boom is intact. This means that the rebound in monetary inflation COULD prolong the boom phase of the current cycle. Whether it actually will is not knowable at this time. One of the ‘tells’ will be whether or not there is a sizable pick-up over the next three months in new manufacturing orders.
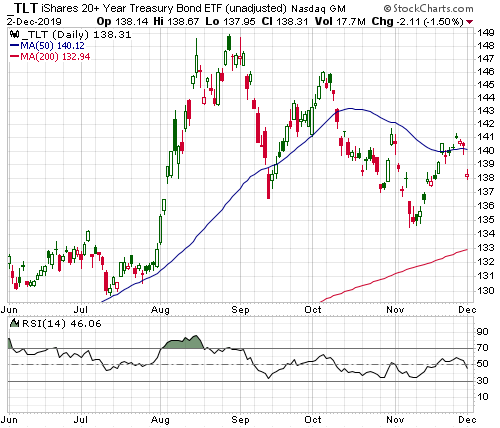
If the boom phase of the cycle is extended by the monetary inflation rebound it will be bullish for oil, industrial metals and the stocks of cyclical companies (the more cyclical the better), and bearish for gold, T-Bonds and “defensive” stocks.