Anyone with rudimentary knowledge of good economic theory can explain why government price controls are a bad idea. It boils down to the fact that the optimum price is the price that naturally balances supply and demand, and to the related fact that forcing the price to be above or below the level at which supply and demand would naturally be in balance will lead to either a glut or a shortage. However, even though most people are capable of understanding why price controls are counter-productive, they still want them.
To be clear, most people living in semi-free countries are undoubtedly against the general concept of price controls, but they will be in favour of specific price controls. In a remarkable display of cognitive dissonance, they will simultaneously understand why price controls must cause economic problems and advocate for price controls in certain situations.
They will be in favour of certain price controls due to political leanings or due to being direct beneficiaries of the controls. Here are some examples:
1) Anyone who understands how supply and demand inter-relate should understand that minimum wage laws are not only counter-productive on an economy-wide basis but also cause the most problems for the group of workers they have supposedly been put in place to protect. In particular, it is axiomatic that if government intervention forces the price of labour to be higher than it would otherwise be then the demand for labour will be lower, that is, more people will be unemployed, with the additional unemployment occurring mostly within the ranks of the lowest-skilled workers. For example, if the official minimum wage is $15/hour and someone, due to their lack of experience or skills, is only worth $12/hour, then that person will be out of work. He might be eager to work for $12/hour to gain the experience/training he needs to increase the value of his labour, but the government says: “No; you will either get paid $15/hour or you will be unemployed”.
There are countless people who understand all this and yet strongly support minimum wage laws, either because the laws mesh with their political beliefs or because they personally benefit from the laws.
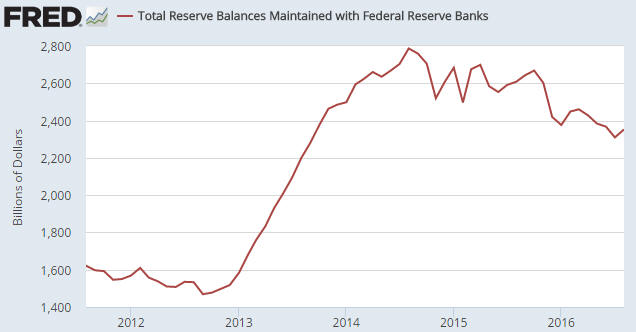
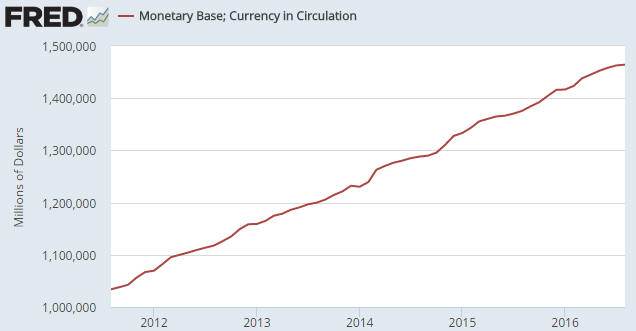
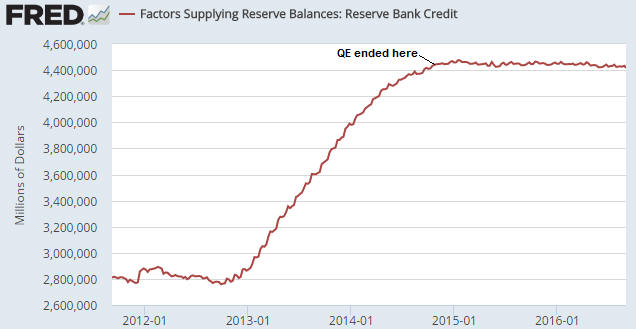
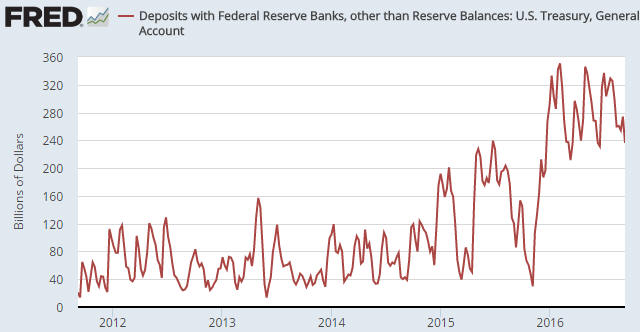
2) Anyone who understands basic economics should be capable of figuring out that it makes no sense for one of the most important prices in the economy to be set by a banking committee or government agency, and yet most people involved in economics and finance believe that there should be a central bank.
3) It is obvious that “rent control” legislation will lead to a shortage of rental properties and lower average standards of maintenance for existing rental properties, but the current/direct beneficiaries of the legislation (the people who live in rent-controlled housing) will often be in favour of this form of price control.
4) Price caps on utility charges will generally seem like a good idea to the people who currently benefit due to having lower electricity or water bills. That will typically be so even if these people have given the matter enough thought to understand that the artificially-low current prices will lead to less investment in future supply and less maintenance on current plant, leading, in turn, to much higher prices and/or a lower level of service in the future.
5) So-called “anti-price-gouging” laws are invariably popular during disasters, but laws that prevent prices from fully responding to a sudden shortage also reduce the incentive to speedily address the shortage. They therefore prolong the supply problem.
6) Here’s an example that I wasn’t aware of until a couple of weeks ago when I read the article posted HERE. The article discusses a dispute between companies that drill for natural gas in the US and landowners who receive royalty payments in exchange for letting the companies drill on their land. The dispute is about whether the drilling companies are entitled to deduct certain expenses from the royalty payments, but what really caught my attention was the reference to a Pennsylvania state law mandating that a landowner must receive a royalty of at least 12.5 percent of the value of the gas produced on his property.
This law was undoubtedly put in place for the benefit of landowners and most landowners are probably in favour of it, but what it means is that if the price of natural gas isn’t high enough to enable the drilling companies to afford a 12.5% royalty then production will stop and the landowners will get nothing. There’s no scope for the royalty payments to be influenced by natural market forces, although it’s possible that the drilling companies are using deductions to get around the law and reduce the effective royalty rate to a level that is economic at the current gas price.
In summary, very few people are consistently opposed to government price controls. Even people who have enough economics knowledge to understand why price controls never work as advertised find reasons to believe in particular price controls. As a consequence, most of the price controls that are now in place have a lot of supporters among the voting public and are therefore likely to remain in place.
 Print This Post
Print This Post