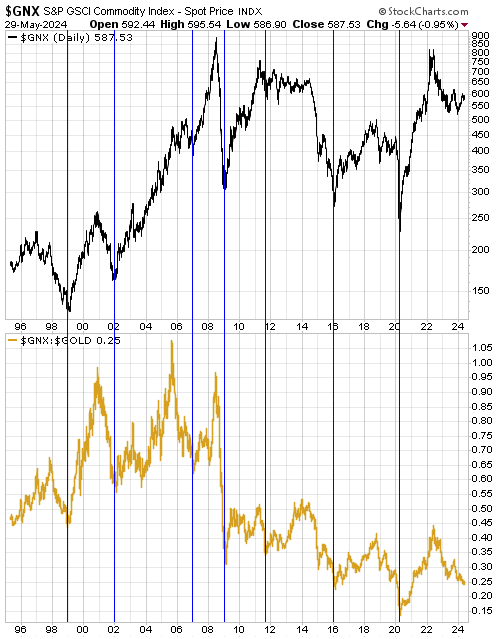
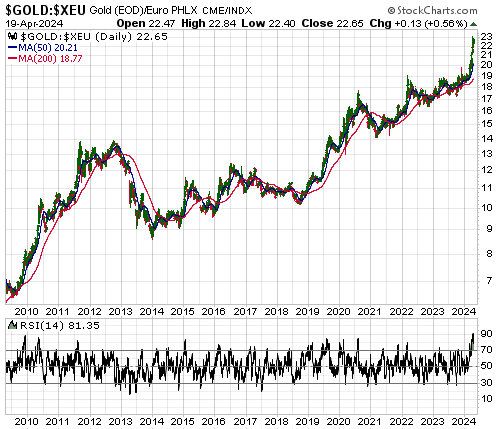
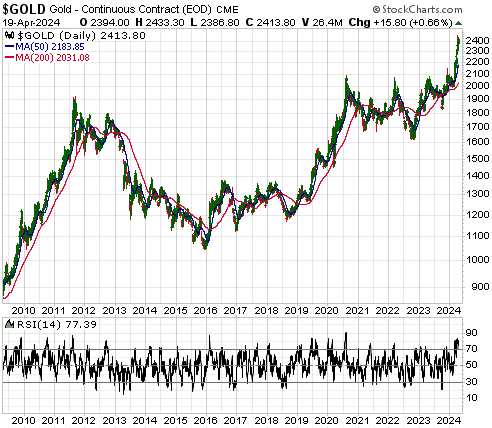
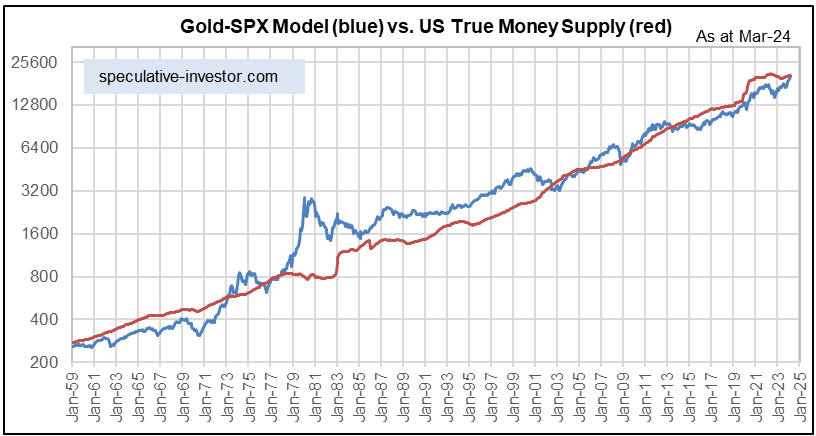
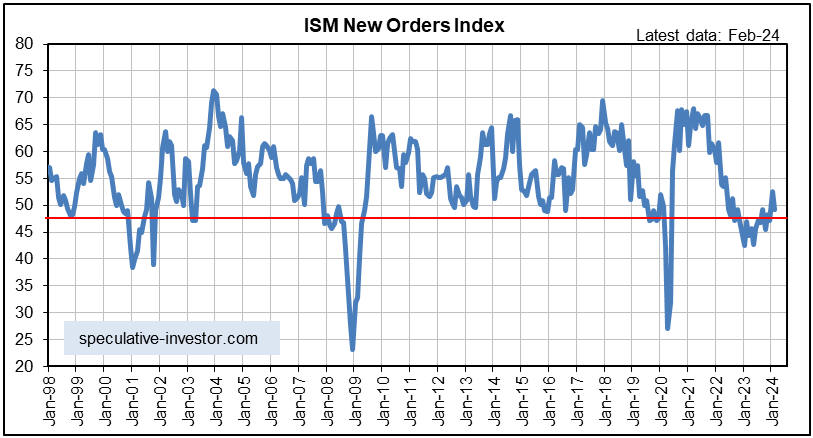
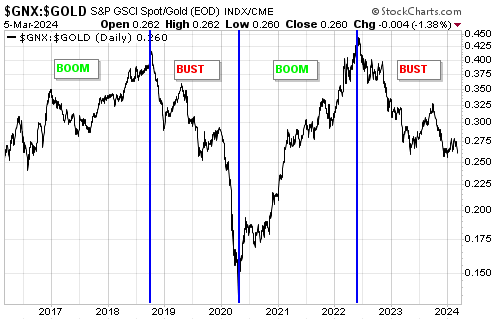
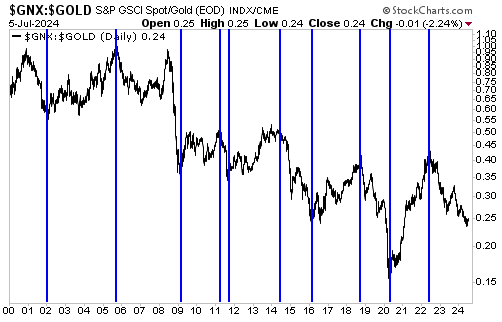[This blog post is an excerpt from a recent commentary at www.speculative-investor.com]
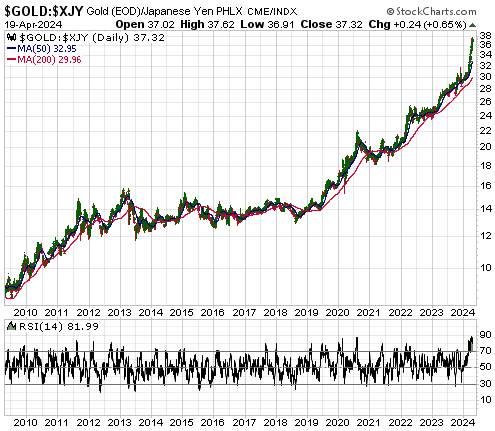
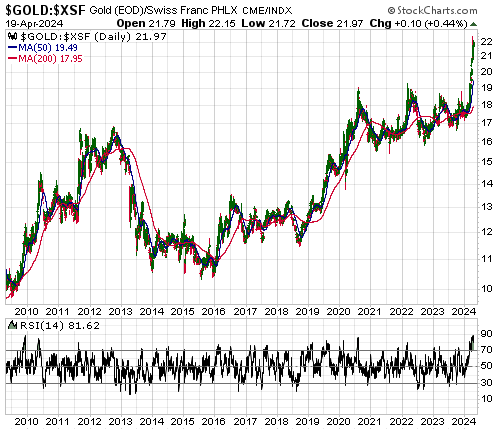
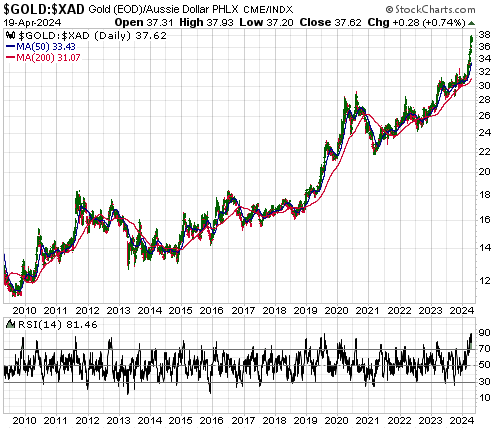
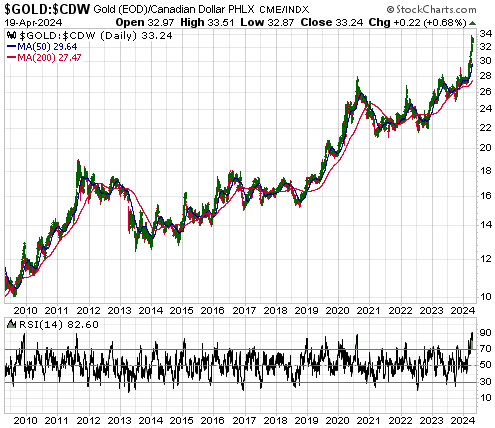
Both Kamala Harris and Donald Trump are espousing policies that will be bearish for the US$ and bullish for gold. This means that regardless of what it turns out to be, the outcome of the November-2024 Presidential Election will be consistent with our view that the US dollar’s foreign exchange value will continue to trend downward and the US$ gold price will continue to trend upward for at least another 12 months. However, apart from having similar ramifications for the longer-term trends in the currency and gold markets, there are substantial differences between the candidates’ main policies. Let’s delve into some of the details.
Harris has talked about raising the capital gains tax rate and introducing a tax on unrealised capital gains to ensure that very wealthy taxpayers pay a minimum tax rate of 25%. If implemented, these changes would have the effect of reducing investment and therefore economic progress. Also, they would be a boon to the IRS and the private tax planning/reporting industry, because the additional complexity introduced by incorporating calculations of unrealised capital gains into taxable income would require substantial extra resources in both the government and the private sector. These extra resources wouldn’t just be non-productive, they would be counterproductive.
As an aside, when politicians introduce new taxes they usually make the assumption that the world will continue as before except with more money being paid to the government. However, taxes change behaviour, sometimes to the extent that new or increased taxes lead to a reduction in government revenue. This is exemplified by the fact that almost every country that has imposed a wealth tax has ended up scrapping the tax because it led to the exodus of capital, resulting in a weaker economy and lower revenue for the government. The reality is that while a promise to extract more money from the extremely wealthy can sound good to many voters, the wealthier a taxpayer the more mobile their wealth tends to be.
Although she has attempted to soften her stance on energy-related issues (for example, she claims to no longer favour a ban on fracking and she has stopped talking about the “Green New Deal” that she once supported), under a Harris regime it’s likely that, as part of a general increase in the amount of government regulation of business, it would be more difficult to get approvals for oil and gas projects. Also, it’s almost certain that the government would direct a lot more resources towards intermittent energy (sometimes called renewable energy). These actions would drive up the price of energy and increase the risk of energy shortages, with knock-on negative implications for the US economy.
Lastly, a Harris administration probably would prolong the Ukraine-Russia war, with devastating additional consequences for Ukraine — and potentially for all of Europe if the war is allowed to escalate — in terms of lives and infrastructure, as well as negative consequences for the US government’s budget deficit. A Trump administration, on the other hand, would be more likely to negotiate a settlement that ends the senseless destruction.
Trump is advocating lower taxes, which would be a plus if he were also advocating government spending cuts to offset the associated reduction in government revenue. However, it seems that no meaningful spending cuts are being considered. Therefore, the tax cuts would accelerate the rate of increase of the federal government’s debt, leading to higher interest rates and private-sector debt being ‘crowded out’ by government debt.
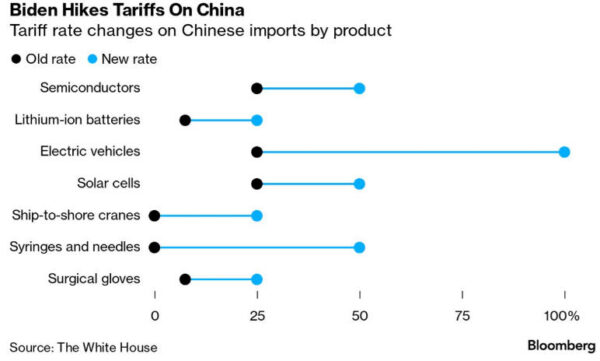
Trump also is advocating tariffs on all imports, with huge tariffs to be imposed on any imports from China. Furthermore, he has stated that he will use tariffs as a weapon against any country that acts in a way that he deems unacceptable, including against any country that attempts to move away from the US$-based international monetary system.
Tariffs that are imposed on US imports are paid by the US-based importers and would get passed on to US consumers, so an effect of the tariffs would be a sizable increase in the US cost of living. Another effect would involve the start of a process to change supply chains and relocate manufacturing in response to the sudden government-forced changes in costs. This process would be long and expensive.
There is no doubt that the Trump tariffs would lead to retaliation from other governments, with predictable effects being smaller markets and smaller profit margins for US companies exporting from the US or operating outside the US. Also, it’s likely that international trade blocs would form that excluded the US.
Most significantly from a long-term perspective, the tariffs and the threat to use tariffs as a weapon to punish governments deemed by the President to be recalcitrant would reduce the international demand for the US$ and could bring forward the demise of the current global monetary system (the Eurodollar System discussed in the 12th August Weekly Update). This is not primarily because the tariffs would lead to less international US$-denominated trading of goods and services, although they certainly would do that. Instead, it is because the non-US demand to hold US dollars is based on the US having large, liquid, open and secure markets. The US financial markets will remain large and liquid for the foreseeable future, but the international demand for the US$ will decline to the extent that these markets are no longer perceived to be open and secure.
The shift away from the US$ would occur over many years, because currently there is no alternative. However, the introduction of Trump’s tariffs would increase the urgency to establish an alternative and could have noticeable effects on the currency market as soon as next year.
By the way, although it was ineffective the Biden administration’s decision in 2022 to ban Russian banks from using the SWIFT system possibly was viewed as a ‘shot across the bow’ by many foreign governments, corporations and wealthy individuals. If Trump gets elected and does what he has said he will do with tariffs, it would be a ‘shot directly into the bow’.
Summarising the above, a Harris administration would attempt to establish higher tax rates, which would lead to reduced investment and a weaker US economy. Also, the price of energy would be higher, more resources would be directed towards inefficient sources of energy and the Ukraine-Russia war probably would either grind on or escalate. A Trump administration wouldn’t make these mistakes, but via aggressive and far-reaching tariffs it would raise the cost of living and throw the equivalent of a giant spanner into the international trading and investing works. One thing that Harris and Trump have in common is that their planned actions will ensure that the US government’s debt burden continues to increase at a rapid pace.
It’s almost as if both sides of the US political aisle have a weaker dollar and a higher gold price as unofficial goals.
 Print This Post
Print This Post