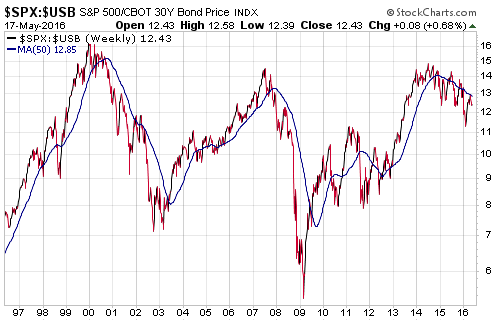
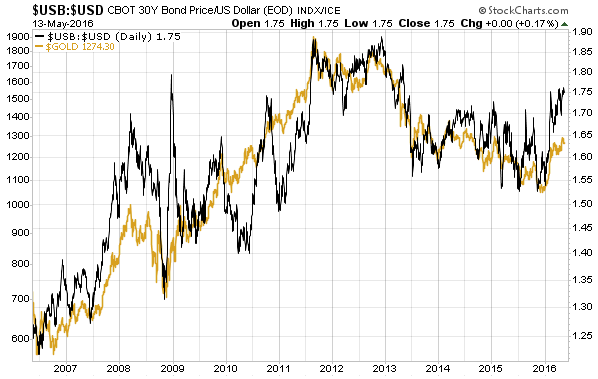
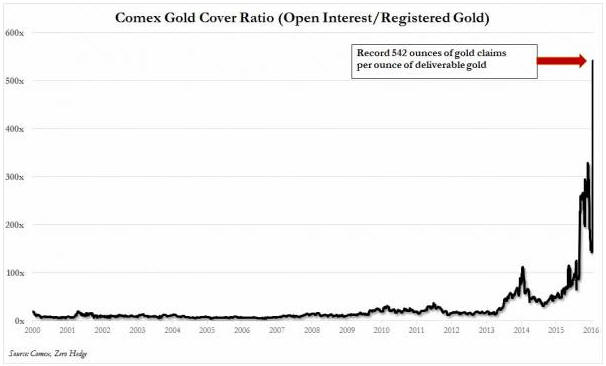
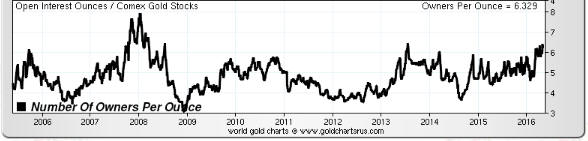
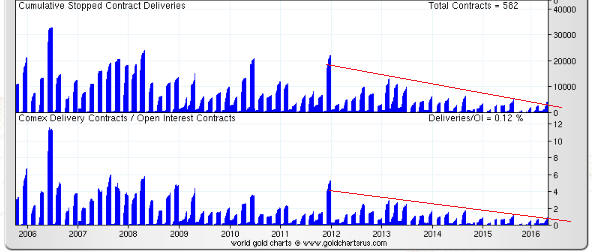
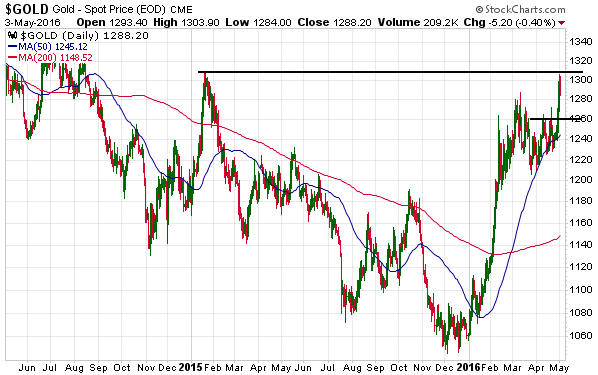
(This post is an excerpt from a commentary published at TSI late last week. Note that an explanation of why a hike in the Fed Funds rate no longer entails monetary tightening can be found in a March-2015 post at the TSI blog.)
In early-November of last year we predicted that a tradable gold rally would begin near the mid-December FOMC Meeting as long as the Fed did what almost everyone was expecting and implemented its first rate hike in more than 8 years. Our reasoning was explained as follows in the 4th November Interim Update:
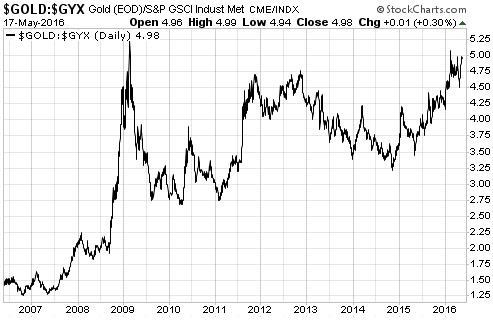
“Looking beyond the knee-jerk reactions to the news of the day, we see a gold market stuck in limbo. In this no-man’s land between a definitively-bullish and a definitively-bearish fundamental backdrop for gold, the US$ gold price works its way higher during periods when it seems that the start of the Fed’s rate-hiking is being pushed out and works its way lower during periods when it seems that the start of the Fed’s rate-hiking is being brought forward.
To get out of this ‘limbo’ and into a situation where a more substantial gold rally is probable, it appears that one of two things will have to happen. Either the Fed will have to take the first step along the rate-hiking path, or the economic/stock-market situation will have to become bad enough that additional monetary easing will be the Fed’s obvious next move. In other words, the Fed will have to stop vacillating and move one way or the other.
Although counterintuitive, there are two good reasons to expect that a Fed rate hike would usher-in a more bullish period for gold. The first reason is that it would potentially be a “sell the rumour buy the news” situation. We are referring to the fact that when a market sells off in anticipation of ostensibly-bearish news, the arrival of the actual news will often lead to a wave of short-covering and an upward price reversal. The second and more interesting reason is that it would spark the realisation that in the current circumstances a Fed rate hike does not entail monetary tightening.”
As it turned out, the Fed went ahead and implemented its first rate hike in mid-December and a strong upward trend in the gold price got underway less than 48 hours later.
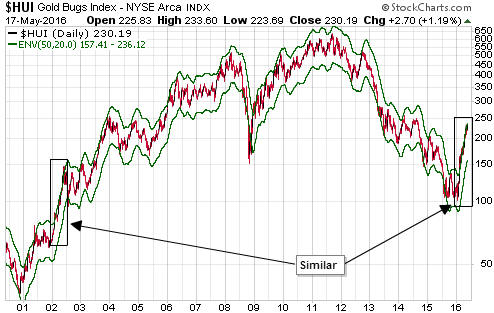
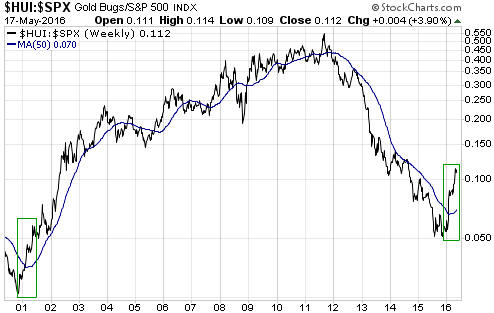
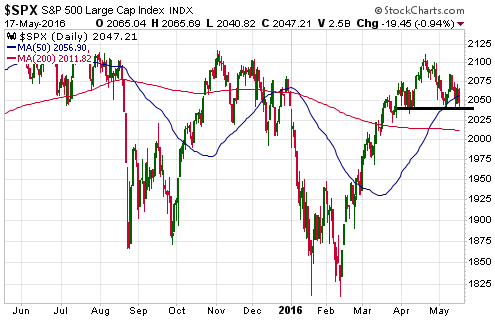
The reason for bringing this up isn’t to brag about getting something right; it’s to point out that gold now appears to be stuck in a similar situation to the one we described on 4th November. As was the case back then, to ignite the next tradable gold rally it appears that the Fed will have to stop vacillating. Either the Fed will have to take its second step along the rate-hiking path or the economic/stock-market situation will have to become bad enough that all thoughts of a 2016 rate hike are wiped out.
 Print This Post
Print This Post