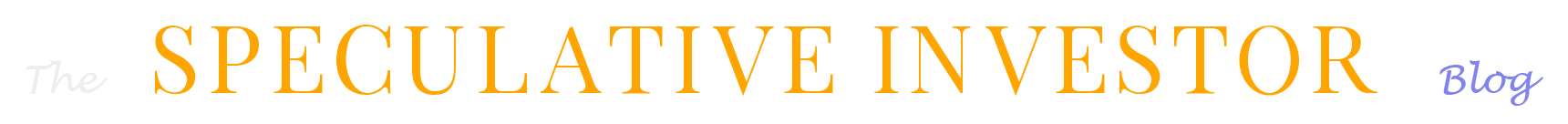There are many problems with the calculation methodology of the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and with the whole concept of coming up with a single number to represent the purchasing power of money. Interestingly, however, if we calculate the inflation-adjusted (‘real’) gold price by dividing the nominal US$ gold price by the US CPI, which is what we have done on the following monthly chart, we see that the result has peaked at around the same level multiple times over the past 50 years and that the current value is around this level. Does this imply that gold’s upside is capped?
It adds to the reasons that we should be cautious about gold’s short-term prospects. These reasons include the size of the speculator net-long position in gold futures, the August-September cyclical turning-point window for the gold mining sector, the likelihood of a reduced pace of US federal government spending during the months following the November-2024 election, the fact that gold’s true fundamentals are not definitively bullish, the high level of the gold/GNX ratio (gold is expensive relative to commodities in general), the extent to which the financial markets have discounted Fed rate cuts (four 0.25% Fed rate cuts are priced-in for 2024, creating the potential for a negative surprise from the Fed), and the high combined value of gold and the S&P500 Index relative to the US money supply. However, we expect that within the next 12 months the gold/CPI ratio will move well into new high territory, mainly because:
1) The US economy finally will enter the recession that has been anticipated for almost two years and that has been delayed by aggressive government spending, leading to efforts by both the Federal Reserve and the federal government to stimulate economic activity.
2) Despite the rise in government bond yields over the past few years, it is clear that neither of the major US political parties nor their presidential candidates have any concern about the level of federal government indebtedness. Putting it another way, currently there is no political will to reduce government spending. On the contrary, both presidential candidates are going down the well-worn path of trying to buy the votes of influential groups while ‘turning a blind eye’ to the government’s debts and deficits.
3) Using our own method of adjusting for the effects of inflation*, which generally will not be accurate in the short-term but should be approximately correct over periods of several years or more, the current ‘real’ gold price is a long way below its 1980 and 2011 highs (our method indicates inflation-adjusted highs of around US$5000/oz in 1980 and US$3400/oz in 2011). Refer to the following monthly chart for more detail.
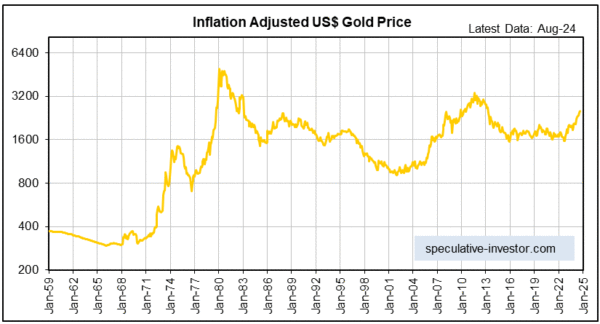
So, while the proximity of the gold/CPI ratio to its long-term resistance adds to the short-term risk, this resistance probably won’t act as a ceiling for much longer.
*The theory that we apply can be summarised as follows: The percentage reduction in a currency’s purchasing power should, over the long-term, be roughly equal to the percentage increase in its supply minus the percentage increase in the combination of population and productivity.