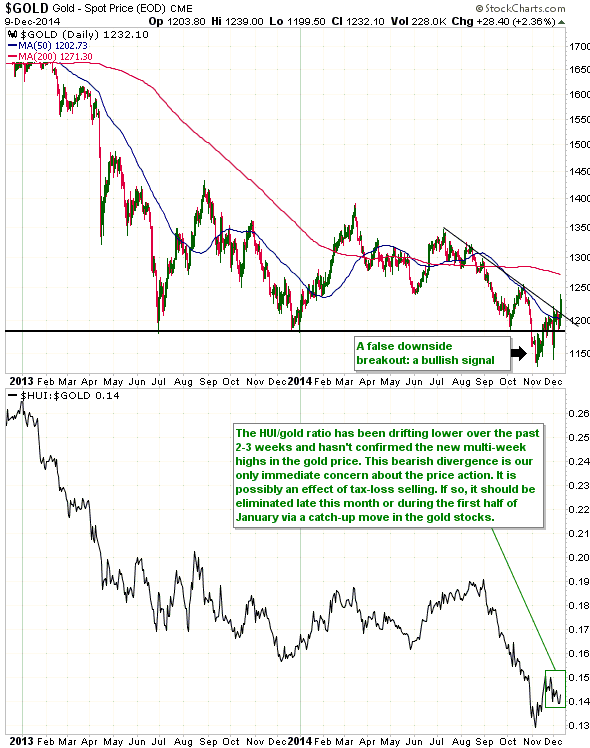
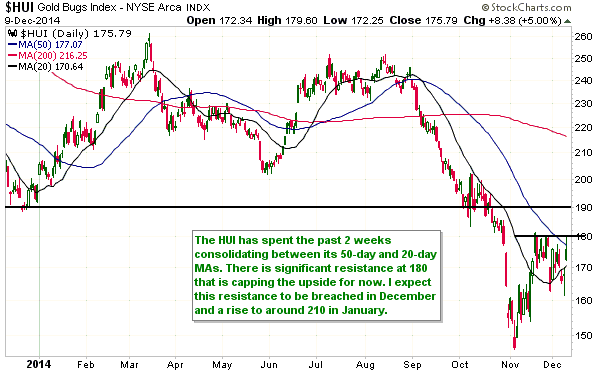
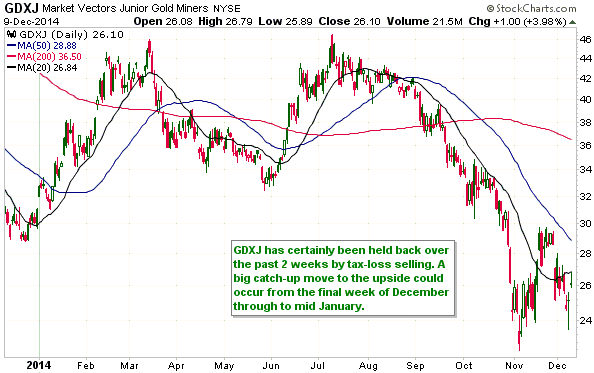
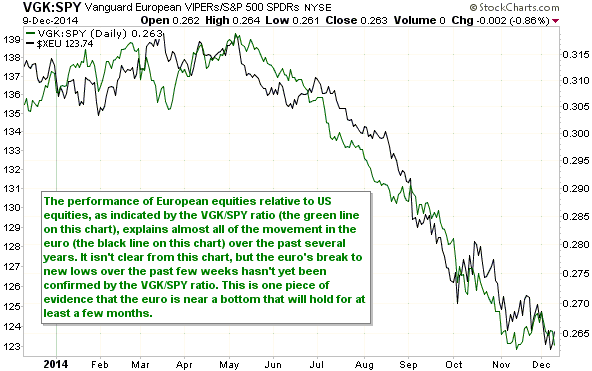
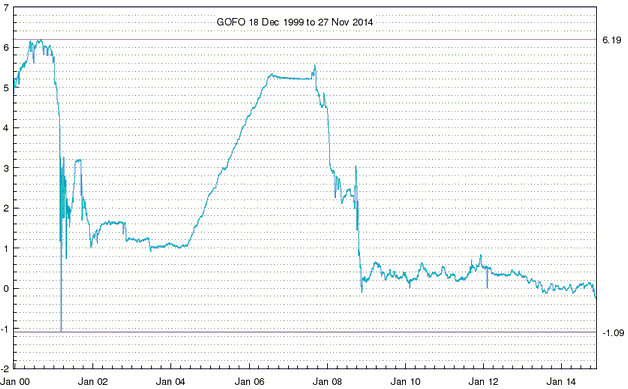
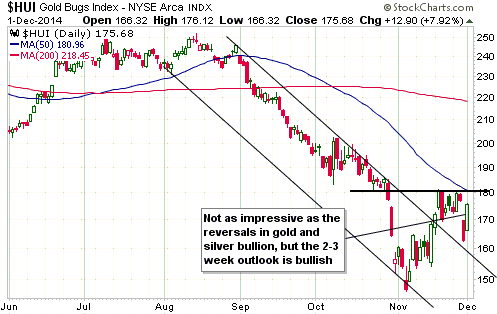
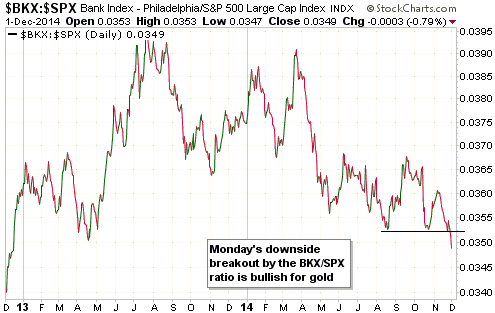
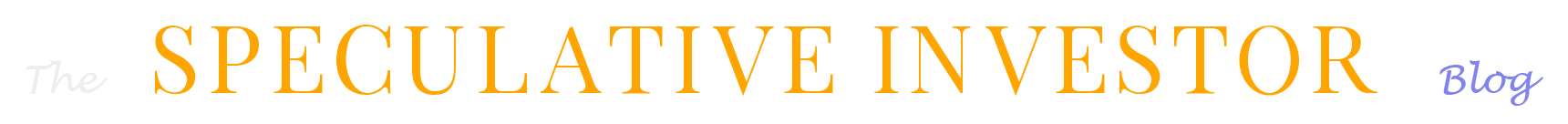Based on Cyclically Adjusted PE (CAPE), Russia’s stock market is the second cheapest stock market in the world. Its current CAPE is around 5, compared to 27.9 for the US. By this measure only the Greek stock market is cheaper, but the Greek stock market has no dividend yield to speak of. Taking into account both CAPE and dividend yield, the Russian market is clearly the world’s cheapest (refer to http://www.starcapital.de/research/stockmarketvaluation for valuation data on many stock markets around the world). This means that it will probably generate outsized returns over the next few years. However, the following chart suggests that it won’t start providing relatively good returns until commodity prices begin trending upwards, regardless of how cheap it gets.
The chart shows that the RSX/EEM ratio (Russian equities relative to Emerging Market equities) trends with the Continuous Commodity Index (CCI). Russia is in the news a lot these days, due to geopolitical issues, economic sanctions and other economic problems, and, at the time of writing this post, a desperate effort to stop the devaluation of the Ruble by hiking the official interest rate from 10.5% to 17%, but it’s the trend in commodity prices that really matters.