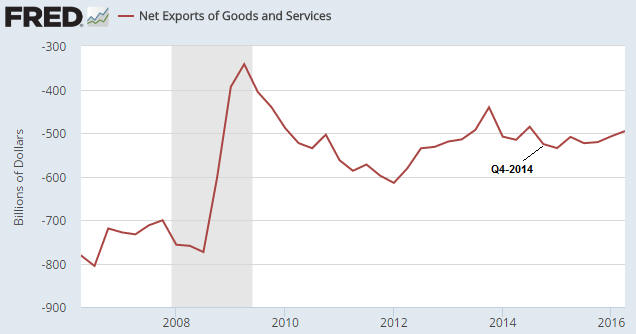
This blog post is a excerpt from a recent TSI commentary.
As the name suggests, the weekly American Association of Individual Investors (AAII) sentiment survey is an attempt to measure the sentiment of individual investors. The AAII members who respond to the survey indicate whether they are bullish, neutral or bearish with regard to the US stock market’s performance over the coming 6 months. The AAII then publishes the results as percentages (the percentages that are bullish, neutral and bearish). The Consensus-inc. survey is a little different in that a) it is based on the published views of brokerage analysts and independent advisory services and b) the result is a single number indicating the bullish percentage. However, the results of both surveys should be contrary indicators because in both cases the surveyed population comes under the broad category affectionately known as “dumb money”.
In other words, in both cases it would be normal for high bullish percentages to occur near market tops (when the next big move is to the downside) and for low bullish percentages to occur near market bottoms (when the next big move is to the upside). That’s why the current situation is strange.
With the S&P500 Index (SPX) having made an all-time high as recently as last month and still being within two percent of its high it would be normal for sentiment to be near an optimistic extreme. As evidenced by the blue line on the following chart, that’s exactly what the Consensus-inc survey is indicating. However, the black line on the following chart shows that the AAII survey is indicating something very different. Whereas the Consensus-inc bullish percentage is currently near the top of its 15-year range, as would be expected given the price action, the AAII bullish percentage is currently near the BOTTOM of its 15-year range. According to the AAII sentiment survey, individual investors are only slightly more bullish now than they were at the crescendo of the Global Financial Crisis in November-2008.
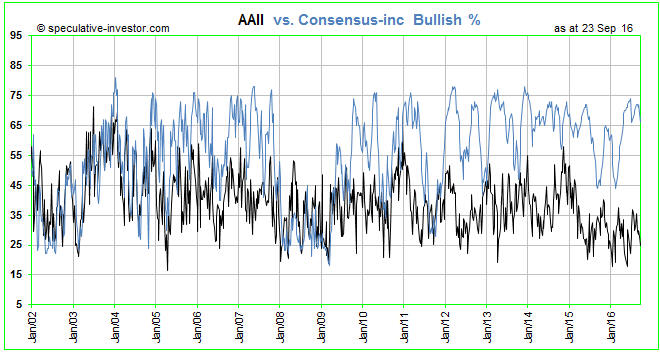
The conflict between the AAII survey results and both the price action and the results of other sentiment surveys (the AAII survey is definitely the ‘odd man out’) suggests that small-scale retail investors have, as a group, given up on the stock market and are generally ignoring the bullish opinions of mainstream analysts and advisors. We are pretty sure that a similar set of circumstances has not arisen at any time over the past 40 years, although it may well have arisen during an earlier period.
The lack of interest in the stock market on the part of small-scale individual investors could be construed as bullish, but we don’t see it that way. To us, the fact that the market has come this far and reached such a high valuation without much participation by the “little guy” suggests that the cyclical bull market will run its course without such participation. It also suggests to us that the cyclical bull market is more likely to end via a gradual rolling-over than an upside blow-off, because upside blow-offs in major financial markets require exuberance from the general public.