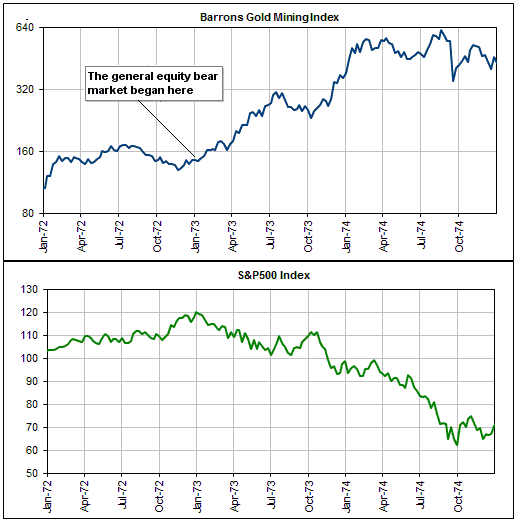
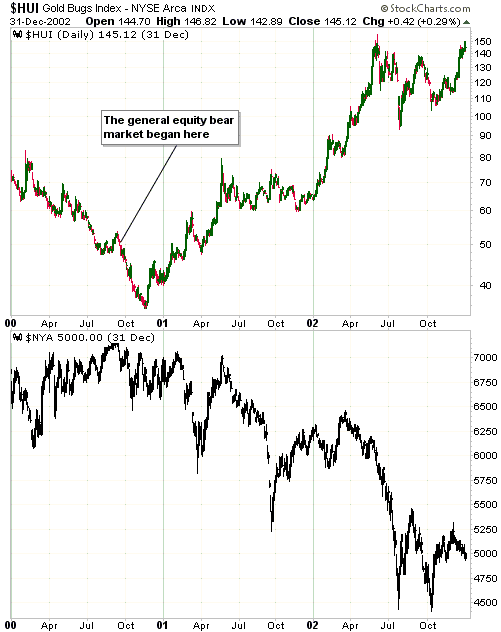
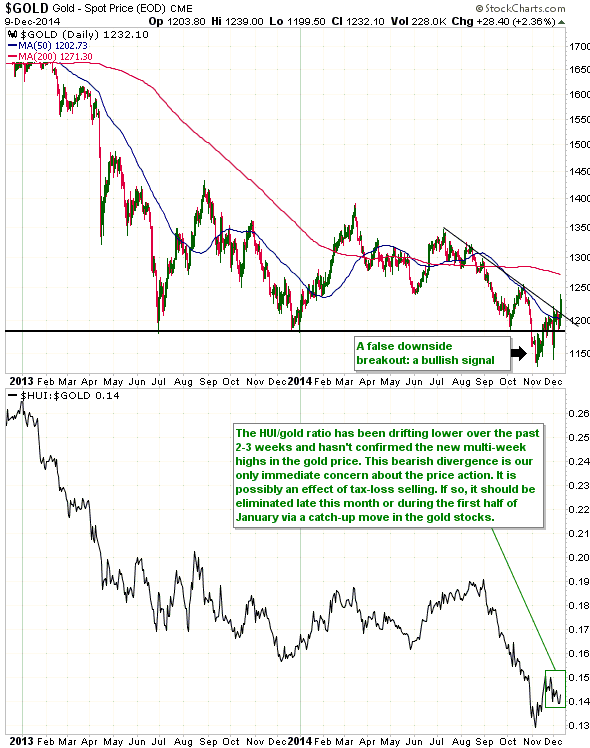
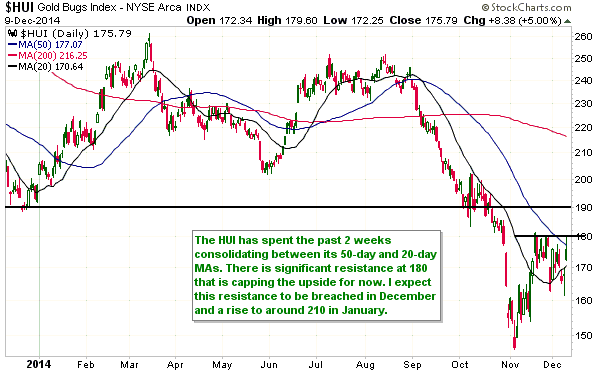
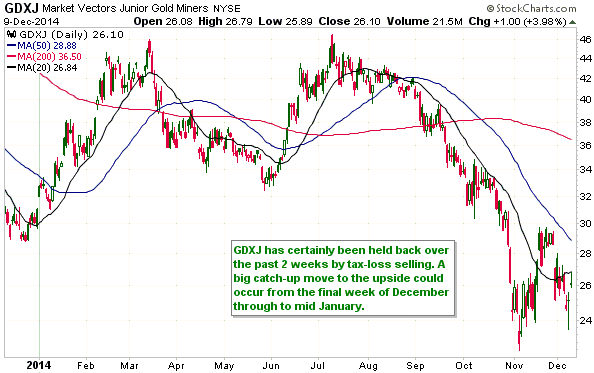
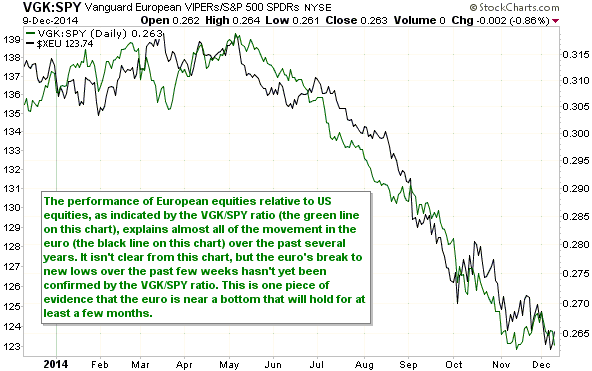
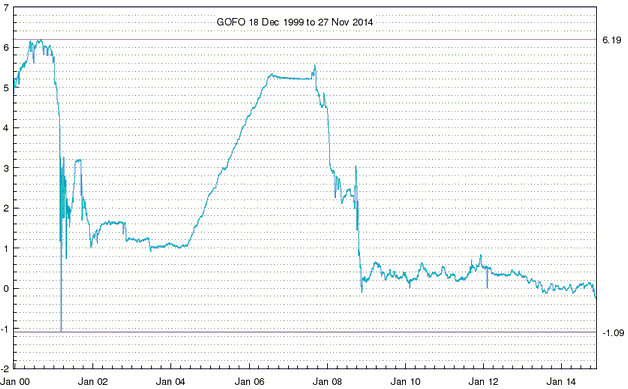
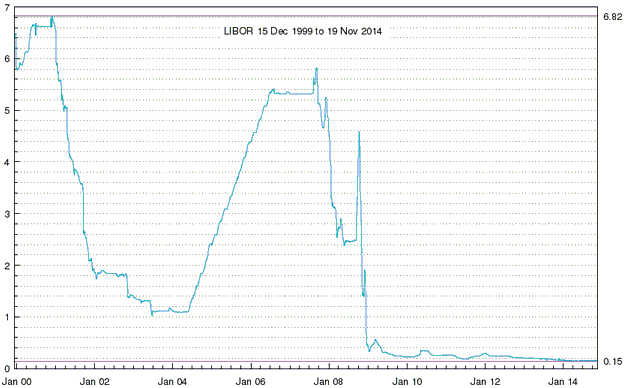
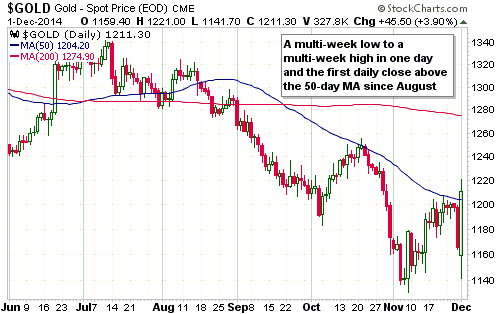
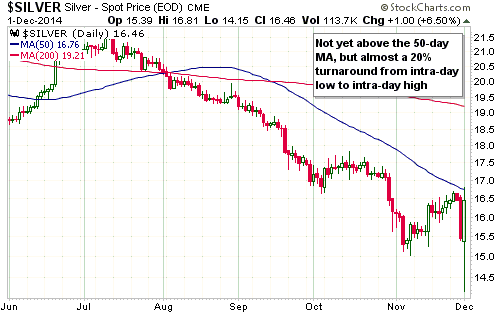
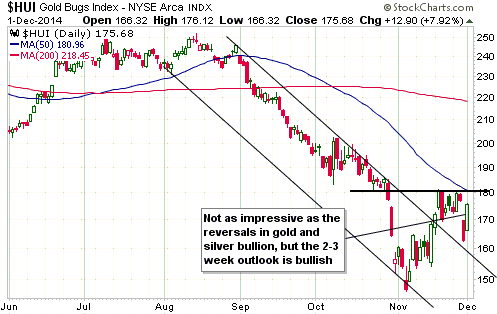
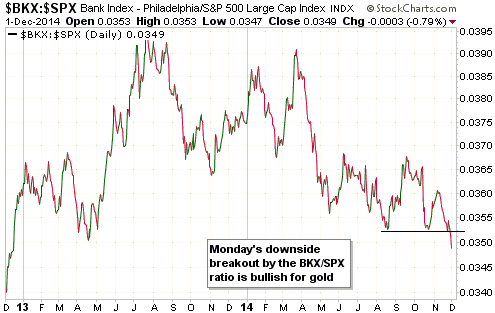
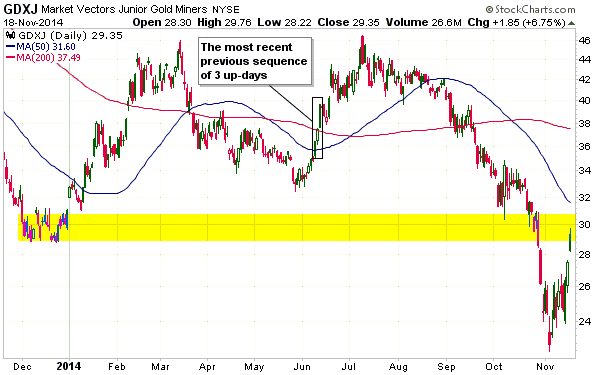
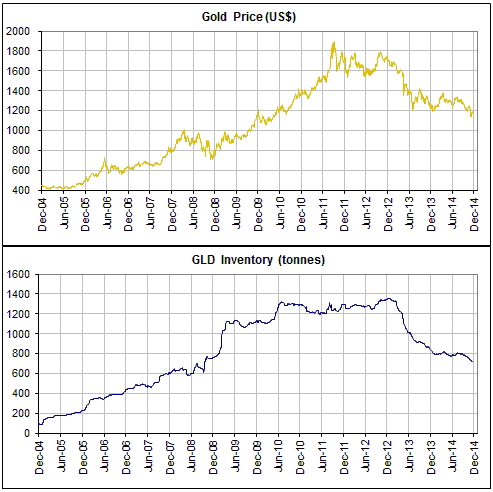
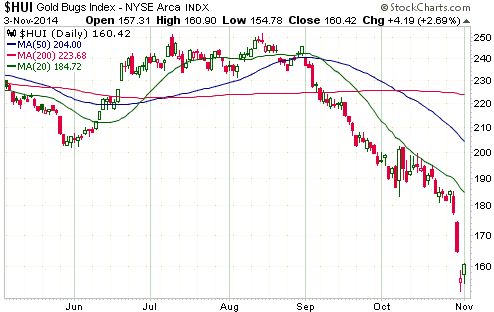
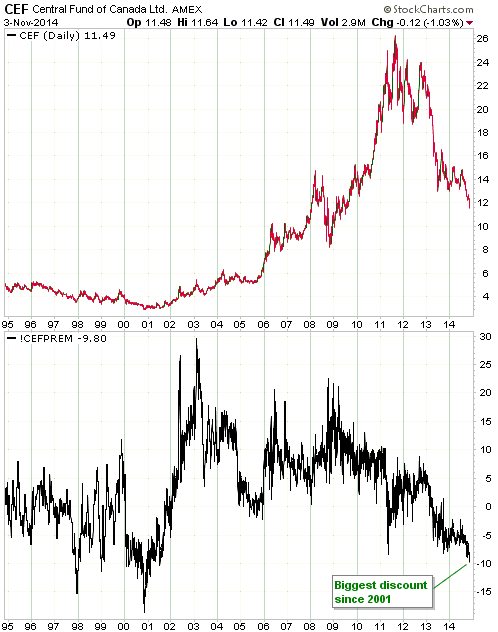
Central banks will continue to create money in response to economic weakness until blatant “price inflation” stops them. This is why the US economic situation is all but guaranteed to deteriorate.
To explain, I point out that if the Fed had done nothing in response to the bust of 2000-2002 then there would have been a severe recession, but the economy would probably have made a full recovery by 2004 and there would have been no mortgage-credit/housing-investment bubble and therefore no 2007-2008 crisis. However, the Fed, in its wisdom and at the behest of intelligent idiots such as Paul Krugman and Paul McCulley, kept interest rates at artificially low levels for years and aggressively ramped up the money supply with the aim of speeding the recovery process. In doing so it fueled a further rapid expansion of debt and a new bubble.
If the Fed had done nothing when this new bubble inevitably burst in 2007-2008 then there would have been a more severe recession, but the US economy would probably have made a full recovery by 2010 or 2011. It would certainly not now be teetering on the verge of another devastating bust.
During 2001-2004 and again since 2008, the Fed felt free to encourage rapid increases in the supplies of money and credit because there were no obvious negative “price inflation” consequences to be seen by those who fixate on price indices such as the CPI. Therefore, the lack of an obvious “price inflation” problem in the US should be viewed as a threat, not a benefit. From the perspective of the people pulling the monetary levers, it provides carte blanche for more money-conjuring in response to economic weakness.
You see, from the collective perspective of the ‘master manipulators’ at the monetary politburo, creating money out of nothing is never a problem until it causes the general price level — which, by the way, can’t be measured, but that doesn’t stop them from pretending to measure it and coming up with figures upon which policies are based — to rise faster than some arbitrary number. They appear to have no inkling that the falsifying of interest rates and relative price signals distorts investment decisions and the structure of production in a way that leads to an economic bust that wipes out all the superficial gains made in response to the so-called monetary stimulus.
If money-pumping continues to be the knee-jerk reaction to every new bout of economic weakness, then a “price inflation” problem will eventually arise. The longer it takes to arise, the greater the amount of damage that will be done in the meantime.
Men of good will should therefore be hoping for an outbreak of “price inflation”, it seemingly being the only way to end the destructive policy-making.
 Print This Post
Print This Post