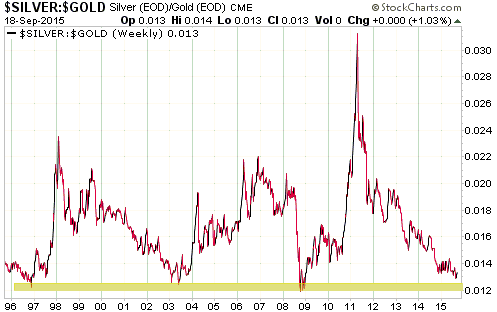
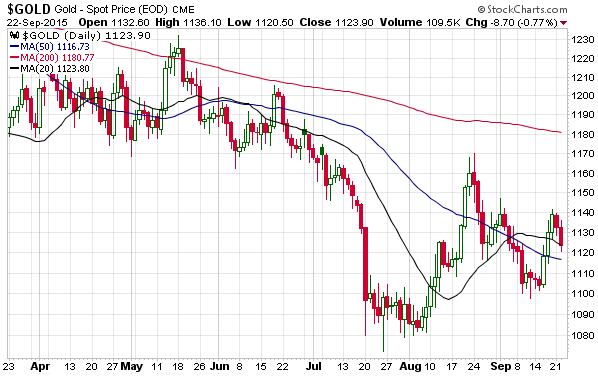
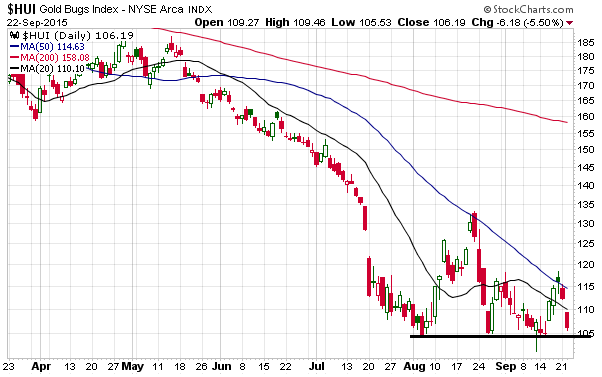
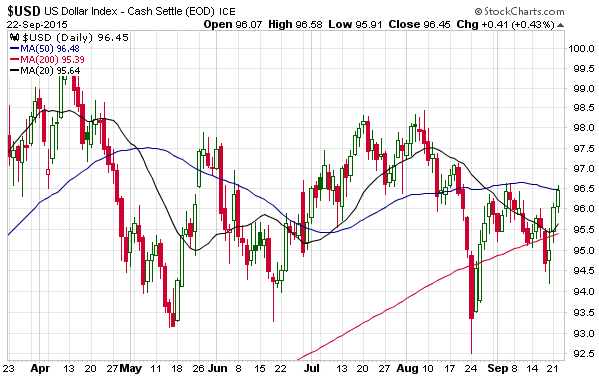
Here’s an unmodified excerpt from a TSI commentary that was published a few days ago. It deals with something that has garnered more attention than it deserves and been wrongly interpreted in some quarters.
We’ve seen some excited commentary about the recent rise in the dollar volume of Reverse Repurchase (RRP) operations conducted by the Fed. Here’s a chart showing the increase in RRPs over the past few years and the dramatic spike that occurred during the final week of September (the latest week covered by the chart).

For the uninitiated, a reverse repurchase agreement is an open market operation in which the Fed sells a Treasury security to an eligible RRP counterparty with an agreement to repurchase that same security at a specified price at a specific time in the future. The difference between the sale price and the repurchase price, together with the length of time between the sale and purchase, implies a rate of interest paid by the Fed on the cash invested by the RRP counterparty. In short, it is a cash loan to the Fed that is collateralised by some of the Fed’s Treasury securities. The Fed receives some cash, the RRP counterparty receives some securities. Note that the Fed never actually needs to borrow money, but it sometimes does so as part of its efforts to control interest rates and money supply.
As mentioned above, the recent large spike in RRPs has caused some excitement. For example, some commentators have speculated that it signals an effort by the Fed to paper-over a major derivative blow-up. As is often the case in such matters, there are less entertaining but more plausible explanations.
We don’t pretend to know the exact reason(s) for the RRP spike, but here are some points that, taken together, go a long way towards explaining it:
1) The Fed recently enabled a much larger range of counterparties to participate in RRPs. Previously it was just primary dealers, but eligible participants now include GSEs, banks and money-market funds.
2) Reverse Repos involve a reduction in bank reserves, which means that the volume of RRPs is limited to some extent by the volume of reserves held at the Fed. Eight years ago the total volume of reserves at the Fed was almost zero, whereas today it is well over $2T. It could therefore make sense to consider the volume of RRPs relative to the volume of bank reserves.
The following chart does exactly that (it shows RRPs relative to total bank reserves at the Fed). Viewed in this way, the recent spike is a lot less dramatic.
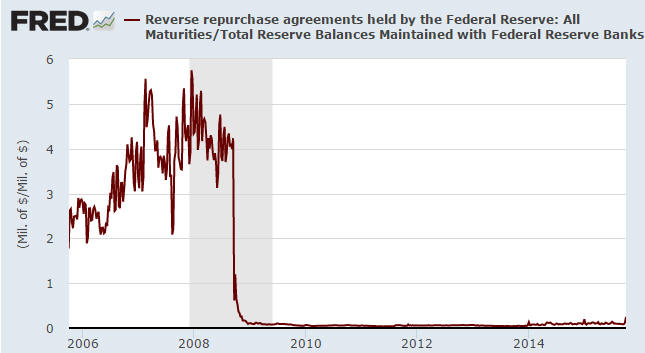
3) Prior to this year RRPs were overnight transactions, but in March of 2015 the FOMC approved a resolution authorizing “Term RRP Operations” that span each quarter-end through January 29, 2016. The Fed has recently been ramping up its Term RRP Operations as part of an experiment related to ‘normalising’ monetary policy.
4) A reverse repo involves the participants parting with the most liquid of assets (cash) for a slightly less liquid asset (Treasury securities), so RRPs are NOT conducted with the aim of boosting financial-system ‘liquidity’. They actually remove liquidity from the financial system.
5) A corollary to point 4) is that because RRPs involve the temporary REMOVAL of money from the financial system, the Fed cannot possibly bail-out or support a bank (or the banking industry as a whole) via RRPs. In effect, a reverse repo is a form of monetary tightening. It is the opposite of “QE”.
6) The recent large increase in the volume of RRPs could be partly due to a temporary shortage of Treasury securities — a shortage that the Fed helped create via its QE and that the US Federal Government has exacerbated by reducing the supply of new securities in response to the closeness of its official “debt ceiling”. That is, the Fed could be using RRPs to alleviate a temporary shortage of government debt securities. However, we suspect that interest-rate arbitrage is playing a larger role, because the RRP participants are getting paid an interest rate that in today’s zero-interest world could look attractive.
7) Lending money to the Fed is the safest way to temporarily park large amounts of cash.
 Print This Post
Print This Post